The Gcode G89 Boring canned cycle with dwell is used for boring and reaming
operation. The G89 boring cycle is same as G85, but the difference between
these two cycles is the G89 will use Dwell at bottom. Some times for boring
operations, when the feedrate is required for the IN and the out directions of
the machined hole, with a specified dwell at the bottom of the hole G89 is
used.
Code line for G89 Boring cycle with dwell:
N100 G98 (G99) G89 X… Y… R… Z… P… F…
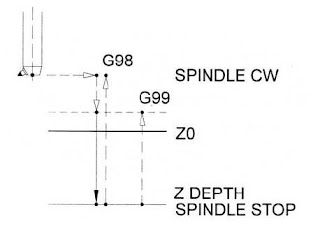
Diagram for G89 Boring cycle with dwell:
Steps for the G89 Boring cycle with dwell:
- Rapid motion to XY position of the hole position.
- Rapid motion to the R level, i.e., to the top of the hole position.
- Feedrate motion to the depth in Z.
- Dwell at the depth – in milli seconds (P).
- Feedrate motion to Z depth.
- Rapid retract to the initial level (with G98) or Rapid retract to R level (with G99).